Antibody Validation Methods for Reliability-KMD Bioscience
In the sphere of life sciences, antibodies serve as indispensable tools, guiding researchers through the maze of cellular and molecular exploration. They act as molecular tags, highlighting specific proteins for detection or manipulation. However, the reliability of the data generated hinges significantly on the accuracy and specificity of these antibodies. Consequently, antibody validation, the process of ensuring that an antibody performs as expected in a specific application, becomes a cornerstone of credible research. There are several methods employed to ascertain the reliability of antibodies, each method examining different aspects of antibody performance.
1 Western Blotting: Western blotting assesses the specificity and sensitivity of antibodies by detecting the presence of target proteins within a complex mixture. It’s pivotal for verifying that an antibody recognizes the correct target protein with high specificity.
2 Immunoprecipitation (IP): IP is another crucial method where antibodies are used to pull down target proteins from a mixture. The effectiveness and specificity of an antibody in IP assays are pivotal for ensuring accurate downstream analyses.
3 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Immunofluorescence (IF): Through IHC and IF, antibodies are used to visualize target proteins within tissue sections or cells. Validation in these assays ensures that the antibody accurately represents the localization and expression level of the target protein.
4 Flow Cytometry: This technique assesses the ability of antibodies to identify and quantify target proteins in a flow of cells, providing insights into the antibody’s effectiveness in recognizing its target under native conditions.
5 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): ELISA evaluates the binding specificity, sensitivity, and quantitative capabilities of antibodies, which is crucial for many diagnostic applications.
6 Knockdown/Knockout Validation: Comparing antibody staining between wild-type and knockdown or knockout cells/tissues provides a robust measure of an antibody’s specificity.
7 Mass Spectrometry: Post IP Mass Spectrometry helps in identifying the proteins that have been pulled down by the antibody, further confirming the antibody’s specificity.
8 Array-based Approaches: Antibodies are screened against a plethora of antigens printed on a microarray slide to evaluate cross-reactivity and specificity.
9 Multiple Antigen Labeling: Utilizing multiple antibodies to different epitopes of the target protein or to other proteins known to be co-localized with the target can provide additional validation.
10 Computational Analysis: In silico analysis utilizing available genomic and proteomic databases can also aid in predicting and evaluating antibody specificity.
This structured examination of antibody validation methods, intertwined with real-world applications and initiatives towards standardization, provides a comprehensive overview of the steps taken to ensure reliability in antibody usage, fostering a culture of excellence and accuracy in scientific investigations.
The meticulous process of antibody validation fortifies the foundation of numerous research projects. It ensures that the deductions made and the knowledge gleaned are standing on solid ground, unfettered by the specter of inaccuracies that could arise from unreliable antibodies. The scientific community has also rallied towards standardizing antibody validation practices. Initiatives like the International Working Group for Antibody Validation (IWGAV) have been pivotal in proposing standardized guidelines for antibody validation, which are steadily gaining traction across the globe.
In conclusion, the essence of antibody validation transcends beyond mere protocol. It is an allegiance to the ethos of scientific accuracy, a commitment to unearthing truths with tools honed to the pinnacle of reliability.
KMD Bioscience’s analysis services take advantage of advanced technology and proven expertise to help customers meet their scientific research project needs. KMD Bioscience can provide protein interaction detection services, including Co-IP, Pull-down and other testing experiments, to reveal the qualitative and quantitative analysis of protein. KMD Bioscience can also carry out ELISA, Western Blot and other commonly used immunological detection techniques to accelerate the research.
For more information, Visit us at https://www.kmdbioscience.com/ to have a detailed understanding.
Join KMD Bioscience on the forefront of biotechnological innovation. Explore the unparalleled possibilities that our technical services bring to your research, and let’s together pave the way for a future of groundbreaking discoveries in immunology and beyond.
References:
1 Bordeaux, J., Welsh, A., Agarwal, S., Killiam, E., Baquero, M., Hanna, J., … & Rimm, D. L. (2010). Antibody validation. Biotechniques, 48(3), 197–209.
Uhlen, M., Bandrowski, A., Carr, S., Edwards, A., Ellenberg, J., Lundberg, E., … & 2 Rockberg, J. (2016). A proposal for validation of antibodies. Nature methods, 13(10), 823–827.
3 Baker, M. (2015). Reproducibility crisis: Blame it on the antibodies. Nature, 521(7552), 274–276.
4 Voskuil, J. L. A. (2014). The challenges with the validation of research antibodies. F1000Research, 3, 154.
5 International Working Group for Antibody Validation (IWGAV) (2016). Antibody Validation: Standards, Policies, and Practices. [Online] Available at: [URL]
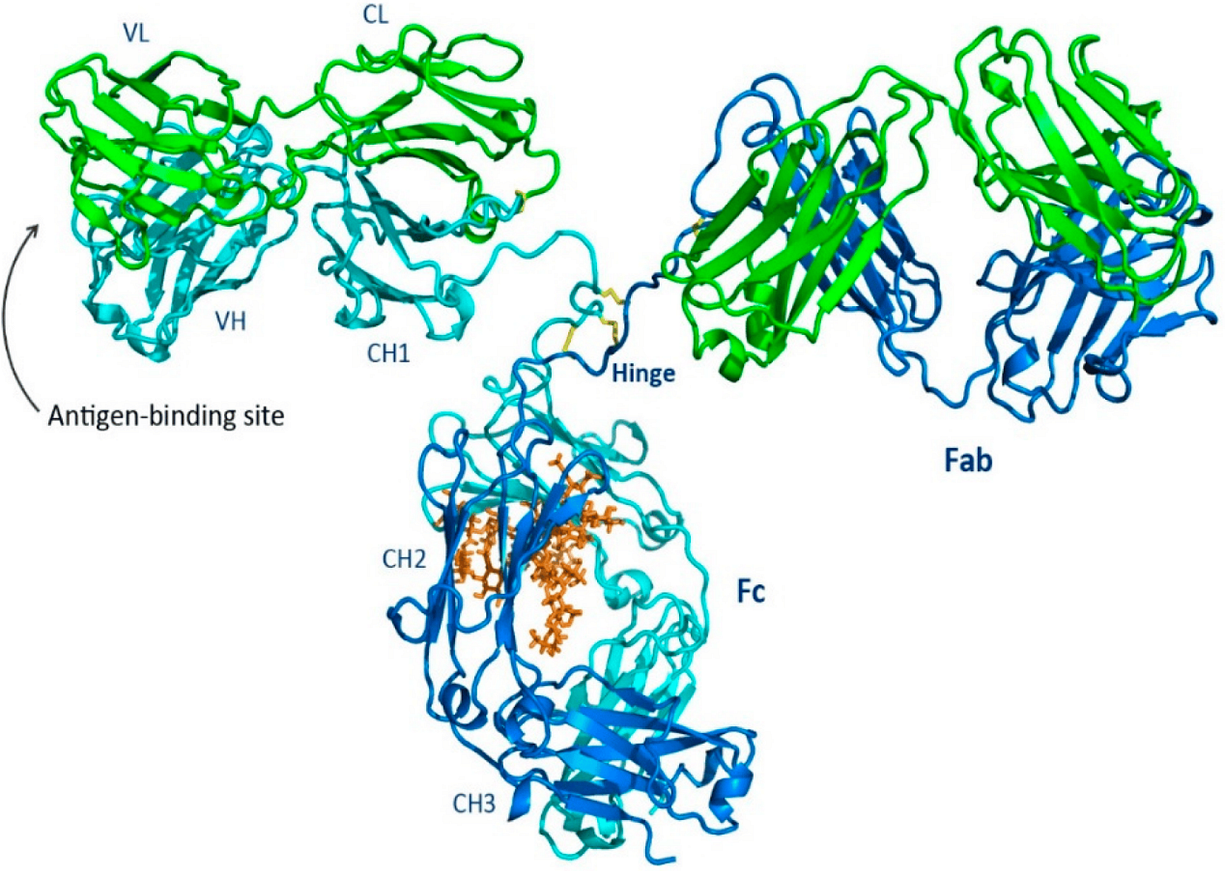
6 Chiu, M.L.; Goulet, D.R.; Teplyakov, A.; Gilliland, G.L. Antibody Structure and Function: The Basis for Engineering Therapeutics. Antibodies 2019, 8, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib8040055
- Like
- Reply
-
Share
About Us · User Accounts and Benefits · Privacy Policy · Management Center · FAQs
© 2025 MolecularCloud